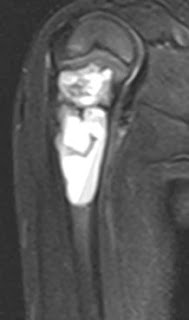
T1 and STIR coronal and sagittal MR images in a 4 year old child showing a fairly well demarcated expansile septate cystic lesion in the proximal metaphyseal region of right humerus. It displays mild heterogeneity but is largely homogenous.
SIMPLE BONE CYST:
-90% occur in long bones, most common in proximal humerus
-Metaphyseal expansile cystic lesion
-May contain "fallen fragment" which is a fractured fragment of bone which moves in dependent part with change in patient position. It is usually seen on x-rays and CT.
-May show fluid-fluid level on CT and MRI
-"Rising bubble sign" : Bubble of gas in non-dependent part of lytic lesion suggestes pathologic fracture. It may be seen on CT and MRI.
-FDG active, may hence mimic metastasis on PET-CT
REFERENCE:
Manaster BJ, Roberts CC, Petersilge CA, Moore S, Hanrahan CJ, Crim J.Diagnostic Imaging Musculoskeletal: Non-traumatic disease. Amirsys.2-206, 2010